Can rapamycin slow the biology of human aging?
Overview
Rapamycin and rapamycin analogs can increase healthy longevity in multiple animal species. However, it remains unknown if this is true for humans. The goal of the Rapalog Pharmacology (RAP PAC) study is to identify a safe and effective dosing scheme to modify the underlying biological processes of human aging. As a part of this study, you will be asked to take rapamycin (sirolimus) or a rapamycin analog (everolimus) once per week for 6 weeks under the research team’s discretion. There will be several assessments before, during, and after the 6 weeks. These include blood and muscle sampling and measurements of body composition and glucose control. All visits are located at the University of Wisconsin-Madison campus. You will be compensated up to $600 for your time.
To participate you must meet the following criteria:
- Men or women between the ages of 55-80
- Free of chronic diseases (i.e., diabetes, dementia, etc.)
- Not taking medications to lower glucose or that prolong bleeding
If you do not know if you meet these criteria, we can evaluate for free.
Participants Will:
- Take a pill once weekly for 6 weeks
- Be monitored by physicians and study team before, during, and after the course of the study. This includes at least one visit per week.
- Complete a variety of health and research tests as shown in the Study Schematic below.
- These include body composition scan (DEXA), blood draw, muscle biopsy, and resting ECG. Participants also have the option to complete glucose assessments such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and/or oral glucose tolerance testing (OGTT).
You will be compensated up to $600 for your time!
Study Schematic
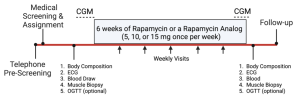
Potential Risks from Study Drug: We are commonly asked about potential risks associated with rapamycin (sirolimus) and the rapamycin analog (everolimus). Like all medications, there are risks of side effects with everolimus and certain medicines that you should not take with everolimus. We will review your current medications (if applicable) to determine your potential eligibility and review the details of potential side effects to ensure that you can make an informed decision on whether to participate or not. Briefly, most side effects are related to the dose used. For patients who need sirolimus or everolimus, it is prescribed at relatively high doses (1.5 to 10 mg per day). Our study uses less frequent dosing schedules (5, 10, or 15 mg once per week) to help minimize the most common risks.
Please contact our study team if you are interested in learning more about the study details or if you have questions:
Email is generally not a secure way to communicate sensitive or health related information as there are many ways for unauthorized users to access email. You should avoid sending sensitive, detailed personal information by email. Email should also not be used to convey information of an urgent nature. If you need to talk to someone immediately or would prefer not to receive study communication by email, please contact the RAPPAC team at 608-228-2554.